Blogs / Knowledge Distillation in Deep Learning: Smart Compression of Neural Models
Knowledge Distillation in Deep Learning: Smart Compression of Neural Models
Introduction
A seasoned professor who has taught at a university for many years, when trying to transfer all of their knowledge and experience to a beginner student in a short amount of time, is essentially doing what Knowledge Distillation achieves in deep learning. This technique enables the knowledge of a large and complex model to be transferred to a smaller and faster one, without a significant loss in quality.
In today's world, where artificial intelligence is rapidly expanding, the need for models that are both accurate and fast is more crucial than ever. Large models like GPT-4 or Claude Sonnet 4 perform exceptionally well, but their size and complexity make using them on mobile devices or resource-constrained systems challenging. Knowledge distillation is a smart solution to this problem.
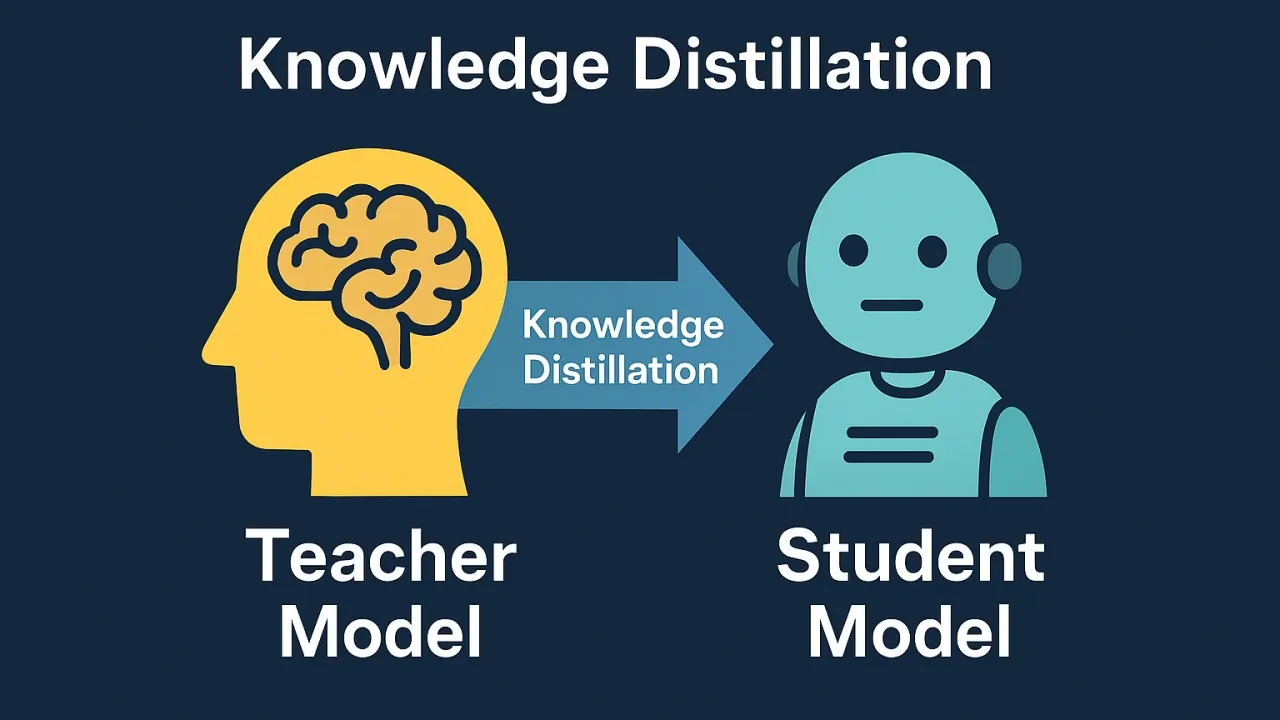
What is Knowledge Distillation?
Knowledge Distillation is a machine learning technique where a small model (called the Student Model) learns from a large, trained model (called the Teacher Model). This process is similar to the teacher-student relationship in the real world, except here, knowledge transfer occurs through mathematical and probabilistic algorithms.
The core idea is that instead of training the small model directly on the original data, we train it using the soft targets output by the large model. These soft targets contain more information than hard labels and help the student model understand more complex relationships between classes.
Practical Example
Suppose you have a large neural network that recognizes animal images with 95% accuracy. This model has 500 million parameters and takes several seconds to run on an average smartphone. Using knowledge distillation, you can create a 10-million-parameter model that recognizes the same image in a fraction of a second with 92% accuracy. This means you've lost only 3% accuracy, but execution speed has increased 50-fold and model size has reduced to one-twentieth!
How Does Knowledge Distillation Work?
Basic Structure
In a typical knowledge distillation scenario, we have two models:
- Teacher Model: A large, complex deep learning model trained on the original dataset with excellent performance.
- Student Model: A smaller model with simpler architecture designed to learn knowledge from the teacher model.
Training Process
The knowledge distillation process typically occurs in several stages:
Stage One: The teacher model is trained on the original training data to achieve the best possible performance. This model is usually a deep neural network with millions of parameters.
Stage Two: For each data sample, the teacher model generates a probability vector showing how likely each class is. These vectors are softened using a parameter called Temperature.
Stage Three: The student model is trained using a combination of two loss functions:
- Hard Loss: Difference between student model predictions and true labels
- Soft Loss: Difference between student model predictions and teacher model's softened output
The Role of Temperature in Knowledge Distillation
Temperature is one of the most important hyperparameters in knowledge distillation. This parameter controls the probability distribution of outputs. With increased Temperature, the probability distribution becomes softer and more uniform, allowing the student model to better learn relationships between different classes.
For example, suppose the teacher model predicts these probabilities for a dog image:
- Dog: 90%
- Wolf: 8%
- Fox: 2%
This additional information (that wolf is more similar than fox) is not present in the hard label (which only says "dog"). Temperature preserves this valuable information.
Types of Knowledge Distillation Methods
1. Response-Based Knowledge Distillation
This is the simplest and most common type of knowledge distillation where only the teacher model's final output is used for training the student model. This method is highly effective for classification problems and relatively simple to implement.
2. Feature-Based Knowledge Distillation
In this method, in addition to the final output, intermediate layers of the teacher model are also used. The student model tries to learn similar feature representations as the teacher model. This method is commonly used in convolutional neural networks for computer vision problems.
3. Relation-Based Knowledge Distillation
This more complex method focuses on relationships between different samples. Instead of just learning the output for each sample, the student model learns how the teacher model relates different samples to each other.
4. Self-Distillation
In this interesting method, a model acts as its own teacher! The model is first trained, then uses its own outputs for retraining and performance improvement. This technique can help improve model generalization.
Amazing Advantages of Knowledge Distillation
Dramatic Model Size Reduction
One of the biggest advantages of knowledge distillation is model compression. In the real world, large language models like GPT-4 may be hundreds of gigabytes in size. Using knowledge distillation, a model of a few hundred megabytes can be built with performance close to the original model.
Practical Example: OpenAI, using techniques similar to knowledge distillation, was able to produce smaller versions of GPT like GPT-4-Mini that are 10 times smaller and 5 times faster, yet still maintain exceptional performance on most tasks.
Increased Inference Speed
Smaller models are naturally faster. In real-time applications like face recognition or natural language processing on mobile devices, speed is crucial. Knowledge distillation allows us to build models that can run in real-time on resource-constrained devices.
Reduced Energy Consumption
Smaller models require less processing power, meaning lower energy consumption. This is especially important in edge devices and IoT where battery is limited.
Improved Generalization
Interestingly, sometimes the student model even performs better than some aspects of the teacher model! This is because the knowledge distillation process acts like a form of regularization and prevents overfitting.
Real-World Applications of Knowledge Distillation
Voice Assistants
Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and AI assistants benefit from knowledge distillation. They must respond to your requests quickly and instantly. Large models aren't suitable for this, but smaller models using knowledge distillation can perform speech recognition quickly and accurately.
Autonomous Vehicles
In the automotive industry, autonomous vehicles must make immediate decisions. They can't wait for a giant model to perform calculations on a server. Using knowledge distillation, small models are installed in vehicles that can detect pedestrians, lane lines, and other vehicles in real-time.
Medical Diagnosis
In medicine and disease diagnosis, large models are trained on millions of medical images. But hospitals and clinics can't always access powerful servers. Smaller models using knowledge distillation can run on regular medical devices and help doctors diagnose diseases like cancer more quickly.
Mobile Phones
Many AI capabilities in smartphones like camera filters, instant translation, or text suggestions use models compressed with knowledge distillation. For example, Google Translate can translate texts offline because it uses small, optimized models.
Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, systems must quickly identify threats. Large models trained on millions of attack samples transfer their knowledge to smaller models that can analyze network traffic in real-time.
Challenges and Solutions
Choosing the Right Architecture
One of the main challenges is selecting the appropriate architecture for the student model. If the model is too small, it can't absorb sufficient knowledge. If too large, the advantage of knowledge distillation is lost.
Solution: Using Neural Architecture Search techniques can help find the best architecture. Efficient architectures like MobileNet or EfficientNet can also be used.
Adjusting Temperature
Finding the optimal Temperature value is an art. Too low a value makes the probability distribution too sharp and transfers little information. Too high a value makes the distribution too uniform and loses useful information.
Solution: Typically, values between 3 and 10 for Temperature work well, but the best value must be found through trial and error.
Balancing Hard and Soft Loss
Determining the appropriate weight for combining hard and soft loss is challenging. If the soft loss weight is too high, the student model may perform poorly on actual labels.
Solution: Typically, a weighting coefficient (usually between 0.5 and 0.9) is used for soft loss, with the remaining weight assigned to hard loss.
Comparing Knowledge Distillation with Other Techniques
| Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages | Main Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Distillation | Maintains high accuracy in small model, transfers implicit knowledge | Requires trained teacher model, time-consuming | Model compression for deployment |
| Pruning | Direct parameter reduction, implementation simplicity | May reduce accuracy, requires fine-tuning | Removing unnecessary weights |
| Quantization | Reduced memory footprint, high execution speed | Reduced computational precision, implementation complexity | Converting weights to lower precision |
| Transfer Learning | Uses pre-learned knowledge, high training speed | Limited to related domains, requires fine-tuning | Using pre-trained models |
| LoRA | Reduces trainable parameters, low memory | Requires specific architecture, limitations in some tasks | Fine-tuning large models |
Advanced Knowledge Distillation Techniques
Multi-Teacher Distillation
In this advanced method, instead of one teacher model, multiple teacher models are used. Each teacher model may specialize in a particular aspect of the task, and the student model learns from all of them.
Practical Example: In a disease diagnosis system, one teacher model might specialize in cancer detection, another in heart diseases, and the student model learns from both to become a comprehensive medical diagnosis system.
Cross-Modal Distillation
This amazing technique refers to knowledge transfer between models with different inputs. For example, a model working on images can transfer its knowledge to a model working on text.
Real Application: In multimodal systems, this technique can help build smart assistants that understand both images and sound.
Progressive Distillation
In this method, instead of direct transfer from a large model to a very small model, this is done gradually. First to a medium model, then to a smaller model.
Online Distillation
Unlike the conventional method where the teacher model is fully trained first, in Online Distillation both models train simultaneously and learn from each other.
Connection with Emerging Technologies
Knowledge Distillation and Small Language Models
With the emergence of Small Language Models (SLM), knowledge distillation has become more important. Companies like Anthropic with Claude Haiku and Google with Gemini Flash use this technique to build models that are both fast and accurate.
Combination with RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with knowledge distillation can create a powerful combination. The small model can learn general knowledge from the large model, then use RAG to access up-to-date information.
Edge AI and Knowledge Distillation
In Edge AI, hardware limitations are critical. Knowledge distillation allows us to build models that can run on IoT devices with limited memory and processors.
Federated Learning and Knowledge Distillation
Federated Learning with knowledge distillation can be useful for preserving privacy while utilizing knowledge from large models. The large teacher model remains on the central server and only its knowledge is transferred to small models on user devices.
Practical Implementation of Knowledge Distillation
Using PyTorch
PyTorch is one of the most popular frameworks for implementing knowledge distillation. Here's a simple example of how to implement it:
python
import torch
Using TensorFlow/Keras
TensorFlow and Keras are also excellent tools for knowledge distillation. Implementation with Keras is very simple and visual.
The Future of Knowledge Distillation
Self-Improving Models
One of the most exciting trends is combining knowledge distillation with self-improving models. These models can continuously learn from new experiences and transfer their knowledge to smaller versions.
Knowledge Distillation in AGI
With progress toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), knowledge distillation will play a key role. AGI systems must be able to quickly and efficiently transfer their knowledge to different modules.
Multi-Task Knowledge Distillation
The future will likely see models that can transfer knowledge for multiple tasks simultaneously. This can help build multi-purpose AI systems.
Knowledge Distillation and Quantum Computing
Combining quantum computing with knowledge distillation could allow us to compress much more complex models and transfer their knowledge to classical models.
Key Points for Success in Knowledge Distillation
- Selecting the Right Teacher Model: The teacher model must perform very well on the intended task. A weak teacher model cannot transfer valuable knowledge.
- Determining Optimal Architecture for Student Model: The student model must have enough capacity to absorb knowledge, but shouldn't be so large that the compression advantage is lost.
- Precise Hyperparameter Tuning: Temperature, hard and soft loss ratio, and learning rate all need careful adjustment.
- Using Data Augmentation: Data Augmentation can help improve student model generalization.
- Continuous Evaluation: Student model performance should be continuously evaluated during the training process to ensure knowledge is being transferred correctly.
Conclusion
Knowledge Distillation is one of the most powerful and practical techniques in modern machine learning. This technique allows us to benefit from the power of large, complex models while having small, efficient models for real-world deployment.
With the ever-growing applications of artificial intelligence in daily life, from smart homes to medical diagnosis and autonomous vehicles, the need for fast, efficient, and accurate models is felt more than ever. Knowledge distillation is a bridge between the world of powerful research models and the practical needs of the real world.
In the future, more advanced knowledge distillation techniques are expected to be developed that can transfer knowledge in more complex ways and with greater efficiency. Combining knowledge distillation with emerging technologies like quantum computing, federated learning, and multimodal models could revolutionize how we use artificial intelligence.
For those who want to work in this field, learning knowledge distillation and related techniques like Fine-tuning, LoRA, and QLoRA is essential. This knowledge can help you create efficient and scalable solutions for real problems.
✨
With DeepFa, AI is in your hands!!
🚀Welcome to DeepFa, where innovation and AI come together to transform the world of creativity and productivity!
- 🔥 Advanced language models: Leverage powerful models like Dalle, Stable Diffusion, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5, GPT-5, and more to create incredible content that captivates everyone.
- 🔥 Text-to-speech and vice versa: With our advanced technologies, easily convert your texts to speech or generate accurate and professional texts from speech.
- 🔥 Content creation and editing: Use our tools to create stunning texts, images, and videos, and craft content that stays memorable.
- 🔥 Data analysis and enterprise solutions: With our API platform, easily analyze complex data and implement key optimizations for your business.
✨ Enter a new world of possibilities with DeepFa! To explore our advanced services and tools, visit our website and take a step forward:
Explore Our ServicesDeepFa is with you to unleash your creativity to the fullest and elevate productivity to a new level using advanced AI tools. Now is the time to build the future together!